Treatments
-
Stroke
At World Stem Cell clinic we have developed a set of protocols to address the patients post stroke needs, including modifications to utilize many adaptive aid, coupled with ongoing physical and occupational therapy, under the supervision of a board certified neurologist and staff. Due to the nature of this disorder it is essential to address the stroke as soon as possible and make certain that you're released and stable to fly. Only your neurologist should make this determination.
Did you know that?
Strokes can be classified into two major categories: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes are those that are caused by interruption of the blood supply, while hemorrhagic strokes are the ones which result from rupture of a blood vessel or an abnormal vascular structure.
-
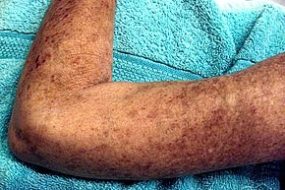
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud’s syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small dilated blood vessels.
-
Parkinson disease (PD)
Parkinson disease (PD) is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms generally come on slowly over time. Early in the disease, the most obvious are shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Thinking and behavioral problems may also occur. Dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Depression and anxiety are also common occurring in more than a third of people with PD. Other symptoms include sensory, sleep, and emotional problems. The main motor symptoms are collectively called “parkinsonism”, or a “parkinsonian syndrome”.
-
PAD
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD), commonly referred to as Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) or peripheral artery occlusive disease (PAOD), refers to the obstruction of large arteries not within the coronary, aortic arch vasculature, or brain. PVD can result from atherosclerosis, inflammatory processes leading to stenosis, an embolism, or thrombus formation. It causes either acute or chronic ischemia (lack of blood supply). Often PAD is a term used to refer to atherosclerotic blockages found in the lower extremity.
Did you know that?
Smoking - tobacco use in any form is the single most important modifiable cause of PVD internationally. Smokers have up to a tenfold increase in relative risk for PVD in a dose-related effect. Exposure to second-hand smoke from environmental exposure has also been shown to promote changes in blood vessel lining (endothelium) which is a precursor to atherosclerosis.
-
Osteoarthritis
(OA) also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease or osteoarthrosis, is a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints,including articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Symptoms may include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, locking, and sometimes an effusion. A variety of causes—hereditary, developmental, metabolic, and mechanical—may initiate processes leading to loss of cartilage. When bone surfaces become less well protected by cartilage, bone may be exposed and damaged. As a result of decreased movement secondary to pain, regional muscles may atrophy, and ligaments may become more lax. Treatment generally involves a combination of exercise, lifestyle modification, and analgesics. If pain becomes debilitating, joint replacement surgery may be used to improve the quality of life.
Did you know that?
OA is the most common form of arthritis, and the leading cause of chronic disability in the United States. It affects about 8 million people in the United Kingdom and nearly 27 million people in the United States.
-
Multiple Sclerosis
New hope to people affected by Multiple Sclerosis !! It is important to be able to consistently produce high-quality stem cells for transplant into patients and World Stem Cell Clinic worldstemcellclinic.com with their past and present research and clinic treatments feel we have a stem cell therapy that can benefit patients with Multiple Sclerosis.
-
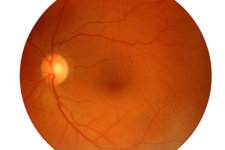
Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a medical condition which usually affects older adults and results in a loss of vision in the center of the visual field (the macula) because of damage to the retina. It occurs in “dry” and “wet” forms. It is a major cause of blindness and visual impairment in older adults (>50 years). Macular degeneration can make it difficult or impossible to read or recognize faces, although enough peripheral vision remains to allow other activities of daily life.
Did you know that?
Age-related macular degeneration begins with characteristic yellow deposits (drusen) in the macula, between the retinal pigment epithelium and the underlying choroid. Most people with these early changes (referred to as age-related maculopathy) have good vision. People with drusen can go on to develop advanced AMD
-
Glaucoma
To treat the loss of vision associated with Glaucoma, the aim would be to either restore the flow of aqueous humour through the trabecular meshwork so as to better regulate the IOP of the eye and/or retard the retinal ganglion cell loss or improve the functional capacity of existing cells.
Did you Know?
The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) has recently declared “restoring vision through regeneration of the retina” as a top priority for eye research over the next 10 years
-
Fuch’s Dystrophy
World Stem Cell Institute worldstemcellinstitute.org in conjunction with World Stem Cell Clinic (India) worldstemcellclinic.com are conducting clinic trials on Fuchs disease “Comparison of endothelial cell layer pre and post Bone Marrow (BM) introduction to cornea” and “pre and post Platelet Rich Plasma/Growth Factors (PRP)”.
-
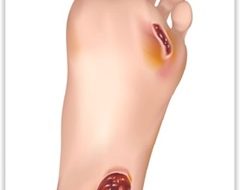
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
“Diabetic foot (DF) is a concomitant illness of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes is one of the main causes of non-traumatic amputation worldwide due to severe peripheral arterial occlusive disease with chronic critical limb ischemia being the most abundant problem. Ulceration occurs as failure of oxygenation, nutrient supply and progressive occlusion of larger blood vessels often exacerbates pre-existing microvascular abnormalities.
-
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes and cognitive impairment.
Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus:
-
Diabetes
After a review of your medical records, a protocol is designed specifically for you. We will determine the best source of stem cells for your current condition. The cells can be found in your bone marrow or adipose (fat), or we will also consider the use of cord blood-derived stem cells.
Did you know that?
Diabetes actually includes any of several metabolic disorders marked by an excessive discharge of urine and persistent thirst, including diabetes mellitus.
-
COPD
Stem Cells COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary disease (COPD), also known as chronic obstructive lung disease(COLD), chronic obstructive airway disease (COAD), chronic airflow limitation (CAL) and chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD), is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases of the lungs in which the airways become narrowed. This leads to a limitation of the flow of air to and from the lungs, causing shortness of breath (dyspnea). In clinical practice, COPD is defined by its characteristically low airflow on lung function tests. In contrast to asthma, this limitation is poorly reversible and usually gets progressively worse over time.
.
Did you know that?
COPD is caused by noxious particles or gas, most commonly from tobacco smoking, which triggers an abnormal inflammatory response in the lung. The inflammatory response in the larger airways is known as chronic bronchitis, which is diagnosed clinically when people regularly cough up sputum.
-
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for the effects of damage to a developing brain by various causes. It is connected with a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness and movement problems. The damage to the brain usually occurs early on in its development, either in the baby during pregnancy or during the period soon after birth. Symptoms may include difficulties in walking, balance and motor control, eating, swallowing, speech or coordination of eye movements. Some people affected by cerebral palsy also have some level of intellectual disability. No two people with cerebral palsy are affected in exactly the same way.
-
Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), also referred to simply as Alzheimer’s, is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and gradually worsens over time. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioural issues. As a person’s condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.
The cause of Alzheimer’s disease is poorly understood. AD affects many different types of neurons in many parts of the brain. This poses a convoluted problem for repairing and/or rejuvenating of the brain. Research does shows that new neurons can be formed but transplanting cells into the brain or signalling-associated proteins is not an easy task.
Diseases Treated
![]()